| Meniscus (anatomy) | |
|---|---|
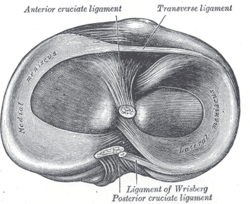
Head of right tibia seen from above, showing menisci and attachments of ligaments
|
|

Left knee-joint from behind, showing interior ligaments
|
|
| Details | |
| Latin | Menisci |
| Identifiers | |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
m_09 |
| TA | A03.0.00.033 |
| FMA | 76690 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In anatomy, a meniscus (from Greek μηνίσκος meniskos, "crescent"[1]) is a crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that, in contrast to articular disks, only partly divides a joint cavity.[2] In humans they are present in the knee, wrist, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints;[3]in other organisms they may be present in other joints.
Generally, the term 'meniscus' is used to refer to the cartilage of the knee, either to the lateral or medial meniscus. Both are cartilaginous tissues that provide structural integrity to the knee when it undergoes tension andtorsion. The menisci are also known as "semi-lunar" cartilages — referring to their half-moon, crescent shape.
Structure[edit]
The menisci of the knee are two pads of fibrocartilaginous tissue which serve to disperse friction in the knee joint between the lower leg (tibia) and the thigh (femur). They are concave on the top and flat on the bottom, articulating with the tibia. They are attached to the small depressions (fossae) between the condyles of the tibia (intercondyloid fossa), and towards the center they are unattached and their shape narrows to a thin shelf.[4]The blood flow of the meniscus is from the periphery (outside) to the central meniscus. Blood flow decreases with age and the central meniscus is avascular by adulthood leading to very poor healing rates.
Function[edit]
The menisci act to disperse the weight of the body and reduce friction during movement. Since the condyles of the femur and tibia meet at one point (which changes during flexion and extension), the menisci spread the load of the body's weight.[5] This differs from sesamoid bones, which are made of osseous tissue and whose function primarily is to protect the nearby tendon and to increase its mechanical effect.
Clinical significance[edit]
Injury[edit]
In sports and orthopedics, people will sometimes speak of "torn cartilage" and actually be referring to an injury to one of the menisci. There are two general types of meniscus injuries, acute tears that are often the result of trauma or a sports injury and chronic or wear-and-tear type tears. Acute tears have many different shapes (vertical, horizontal, radial, oblique, complex) and sizes. They are often treated with surgical repair depending upon the patient's age as they rarely heal on their own. Chronic tears are treated symptomatically: physical therapy with or without the addition of injections and anti-inflammatory medications. If the tear causes continued pain, swelling, or knee dysfunction, then the tear can be removed or repaired surgically.
The Unhappy Triad is a set of commonly co-occurring knee injuries which includes injury to the medial meniscus.
Non-surgical treatment[edit]
Non-surgical treatment is often considered first for a smaller or chronic tear that does not appear amenable to surgical repair. It consists of activity modification, physical therapy for strengthening and range of motion, electro-acupuncture, weight loss, and possibly injections or medications.
Surgical treatment[edit]
Two surgeries of the meniscus are most common. Depending on the type and location of the tear, the patient's age, and physician's preference, injured menisci are usually either repaired or removed, in part or completely (meniscectomy). Each has its advantages and disadvantages. Many studies show the meniscus serves a purpose and therefore doctors will attempt to repair when possible. However, the meniscus has poor blood supply, and, therefore, healing can be difficult. Traditionally it was thought that if there is no chance of healing then it is best to remove the damaged and non-functional meniscus. This has been found to be wrong in some cases in at least one study.[6]
Additional images[edit]
See also[edit]
- Meniscal cartilage replacement therapy
- Discoid meniscus
- Anterior cruciate ligament
- Meniscus transplant
References[edit]
- ^ μηνίσκος, "small moon", is diminutive of μήνη, "moon", from the root ma-, "measure", which reflects the fact the time was measured according to the phases of the moon. The word was also used for curved things in general, such as a necklace or a line of battle. (Lexicon of Orthopaedic Etymology, p 199)
- ^ Platzer (2004), p 208
- ^ .Meniscus, Stedman's (27th ed.)
- ^ Gray's (1918), 7b
- ^ Cluett, Meniscus Tear — Torn Cartilage
- ^ Sihvonen, Raine; Mika Paavola, M.D., Ph.D., Antti Malmivaara, M.D., Ph.D., Ari Itälä, M.D., Ph.D., Antti Joukainen, M.D., Ph.D., Heikki Nurmi, M.D., Juha Kalske, M.D., and Teppo L.N. Järvinen, M.D., Ph.D (December 26, 2013). "Arthroscopic Partial Meniscectomy versus Sham Surgery for a Degenerative Meniscal Tear". The New England Journal of Medicine 369 (26): 2504–2514. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1305189. PMID 24369076. Retrieved 2014-04-04.
- Sources
- "Meniscus". Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th edition. eMedicine - Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2003. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- Cluett, Jonathan (February 10, 2008). "Meniscus Tear — Torn Cartilage". About.com. Retrieved 2008-02-20.
- Diab, Mohammad (1999). Lexicon of Orthopaedic Etymology. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 90-5702-597-3.
- Gray, Henry (1918). "7b. The Knee-joint". Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body. Retrieved 2008-02-20.[broken citation]
- Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.



